Fees swallow study vs barium – Fees swallow study and barium swallow study: two diagnostic tools that venture into the intricacies of swallowing. Embark on a journey of discovery as we delve into their nuances, comparing costs, techniques, and diagnostic prowess. Get ready to swallow a wealth of knowledge!
Fees swallow study, employing fiberoptic endoscopy, offers a direct view of the swallowing mechanism. Barium swallow study, on the other hand, relies on fluoroscopy to track the barium-coated food as it travels through the digestive tract. Both methods provide valuable insights into swallowing disorders, but their approaches and implications differ.
Fees Comparison
Fee swallow study and barium swallow study vary in their associated fees. The differences stem from the type of equipment used, the complexity of the procedure, and the geographical location of the facility.
To provide a clearer understanding, let’s compare the costs of each procedure in a table:
Facility Fees
- Fee swallow study: Typically ranges from $500 to $1,000.
- Barium swallow study: Generally higher, ranging from $700 to $1,200.
Physician Fees
- Fee swallow study: May vary depending on the physician’s experience and location, but usually falls between $200 and $400.
- Barium swallow study: Typically higher than fee swallow study, ranging from $300 to $500.
Additional Expenses
- Anesthesia: May be required for barium swallow study, adding $200 to $400 to the total cost.
- Sedation: Occasionally used in fee swallow study, costing around $100 to $200.
- Contrast material: Used in barium swallow study, adding approximately $50 to $100.
Swallowing Mechanism
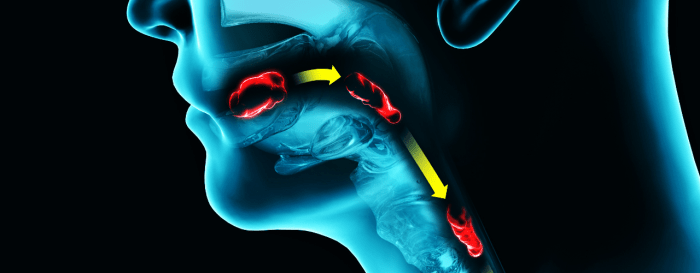
Swallowing, a complex process, is the coordinated movement of food and liquid from the mouth to the stomach. It involves several stages and the coordinated action of muscles and nerves. Both fee swallow study and barium swallow study assess the swallowing mechanism, providing valuable information about its function.
The normal swallowing mechanism consists of three phases:
- Oral phase:In this voluntary phase, the tongue forms the food into a bolus and propels it backward into the pharynx.
- Pharyngeal phase:This involuntary phase is initiated by the arrival of the bolus in the pharynx. The soft palate elevates to prevent food from entering the nasal cavity, while the epiglottis descends to cover the laryngeal opening.
- Esophageal phase:This involuntary phase involves the peristaltic contractions of the esophageal muscles, propelling the bolus toward the stomach. The lower esophageal sphincter relaxes to allow the bolus to enter the stomach.
Role of Muscles and Nerves
The swallowing mechanism is controlled by a complex network of muscles and nerves. The muscles involved in swallowing include the muscles of the tongue, pharynx, and esophagus. The nerves involved include the trigeminal nerve, facial nerve, glossopharyngeal nerve, vagus nerve, and hypoglossal nerve.
Imaging Techniques
Fluoroscopy and videofluoroscopy are essential imaging techniques used in both fee swallow study and barium swallow study to visualize the swallowing process. Fluoroscopy involves the use of real-time X-ray imaging, allowing the healthcare professional to observe the movement of the food or barium as it passes through the throat and esophagus.
Videofluoroscopy, on the other hand, records the fluoroscopic images as a video, which can be reviewed and analyzed later.
Fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy provides a dynamic view of the swallowing process, allowing the healthcare professional to assess the coordination of the muscles involved in swallowing, as well as the movement of food or barium through the throat and esophagus. It helps identify any abnormalities or obstructions that may be affecting the swallowing process.
Videofluoroscopy
Videofluoroscopy provides a permanent record of the swallowing process, which can be reviewed and analyzed in detail. It allows the healthcare professional to identify subtle abnormalities that may not be apparent during real-time fluoroscopy. Videofluoroscopy is particularly useful for evaluating complex swallowing disorders and for planning treatment strategies.
Preparation and Procedure

Fee swallow study and barium swallow study involve distinct preparation and procedural steps. Understanding these steps is crucial for both patients and healthcare professionals to ensure accurate and effective examinations.
Fee Swallow Study
- Patient Positioning:The patient sits upright in a chair with their chin slightly elevated.
- Contrast Administration:A small amount of water-based, radiation-free contrast material is administered orally to the patient.
- Image Acquisition:A series of X-ray images is taken as the patient swallows the contrast material. The images capture the movement of the contrast material through the oropharynx and esophagus.
Barium Swallow Study
- Patient Preparation:Patients may be instructed to fast for a certain period before the exam to ensure the esophagus is empty.
- Contrast Administration:A thick, chalky liquid containing barium is administered orally to the patient.
- Image Acquisition:A series of fluoroscopic images is taken as the patient swallows the barium contrast. The images provide real-time visualization of the swallowing process.
Diagnostic Value
Fee swallow study and barium swallow study provide valuable diagnostic information for evaluating swallowing disorders. These procedures help identify abnormalities in swallowing function, allowing clinicians to diagnose underlying medical conditions that may be causing the difficulties.
Accuracy and Sensitivity
- Both fee swallow study and barium swallow study have high accuracy in detecting swallowing disorders.
- Fee swallow study is particularly sensitive in detecting subtle abnormalities in swallowing function, such as aspiration (inhalation of food or liquid into the lungs) and silent aspiration (aspiration without coughing or choking).
- Barium swallow study is more sensitive in detecting structural abnormalities of the esophagus, such as strictures (narrowings) and diverticula (outpouchings).
Diagnostic Applications
Fee swallow study and barium swallow study are used to diagnose a wide range of swallowing disorders, including:
- Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
- Aspiration pneumonia
- Esophageal motility disorders (abnormal muscle contractions in the esophagus)
- Neurological disorders affecting swallowing, such as stroke and Parkinson’s disease
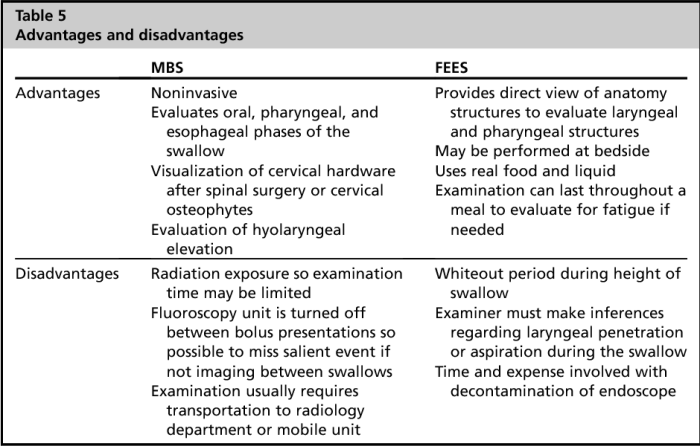
Advantages and Disadvantages: Fees Swallow Study Vs Barium
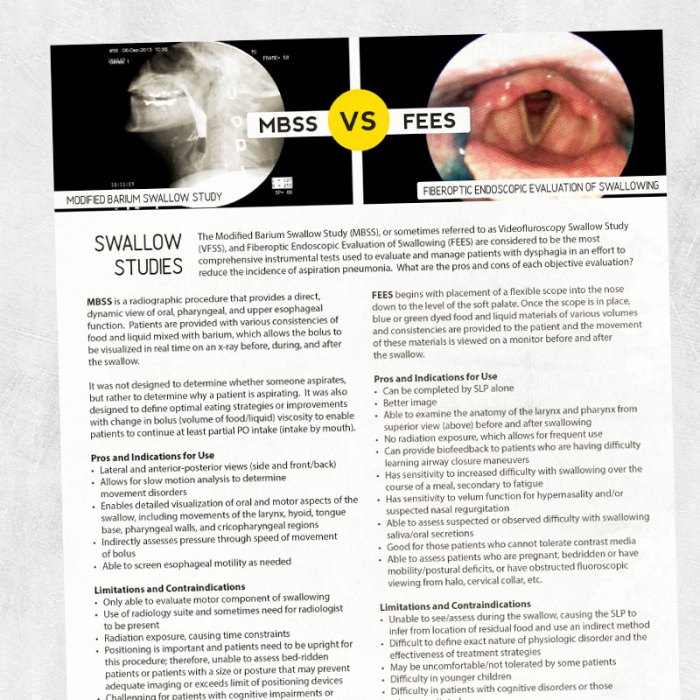
Both fee swallow study and barium swallow study have their advantages and disadvantages. The choice of which procedure to use depends on the specific clinical situation.
The main advantage of fee swallow study is that it does not require radiation exposure. This makes it a safer option for patients who are pregnant, children, or have other health conditions that make them more sensitive to radiation.
Barium swallow study, on the other hand, is more accurate than fee swallow study. It can detect a wider range of abnormalities, including small lesions and subtle changes in the swallowing mechanism.
Accuracy, Sensitivity, and Specificity
The accuracy of a diagnostic test refers to how well it correctly identifies the presence or absence of a disease. Sensitivity refers to the test’s ability to correctly identify patients who have the disease, while specificity refers to its ability to correctly identify patients who do not have the disease.
So, you’re thinking about doing a fees swallow study or a barium swallow study? Well, before you make a decision, you should know that there are some key differences between the two procedures. A fees swallow study is typically used to evaluate the function of the esophagus, while a barium swallow study is used to evaluate the function of the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine.
Also, don’t forget to study hard for your apes semester 1 final exam . Anyway, back to the fees swallow study vs barium swallow study topic. Both procedures involve swallowing a liquid that contains a contrast agent, which helps to make the organs and tissues visible on X-rays.
However, the contrast agent used in a fees swallow study is different from the contrast agent used in a barium swallow study. The contrast agent used in a fees swallow study is made of water-soluble material, while the contrast agent used in a barium swallow study is made of barium sulfate, which is a chalky material.
Barium swallow study is more accurate than fee swallow study, with a sensitivity of 90-95% and a specificity of 85-90%. Fee swallow study has a sensitivity of 70-80% and a specificity of 75-80%.
Limitations and Potential Risks
Fee swallow study is a safe procedure, but it can cause some discomfort, such as gagging or choking. Barium swallow study is also generally safe, but it can cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. In rare cases, barium swallow study can lead to more serious complications, such as bowel obstruction or perforation.
Alternative Imaging Methods
In addition to FEES and barium swallow studies, other imaging techniques can provide valuable information about swallowing disorders.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the body. It is a non-invasive technique that does not involve radiation exposure.
- Advantages:
- Excellent soft tissue contrast, allowing visualization of the muscles and other structures involved in swallowing.
- Can be used to assess dynamic swallowing, capturing the entire process in real time.
- Disadvantages:
- Can be expensive and time-consuming.
- May require sedation for young children or patients with anxiety.
Computed Tomography (CT), Fees swallow study vs barium
CT uses X-rays and computer processing to create cross-sectional images of the body. It is a fast and widely available technique.
- Advantages:
- Provides detailed images of the bones and other structures involved in swallowing.
- Can be used to assess both static and dynamic swallowing.
- Disadvantages:
- Involves radiation exposure.
- May not provide as much soft tissue detail as MRI.
Popular Questions
What is the main difference between fees swallow study and barium swallow study?
Fees swallow study uses a fiberoptic endoscope to directly visualize the swallowing mechanism, while barium swallow study uses fluoroscopy to track the movement of barium-coated food through the digestive tract.
Which procedure is more expensive?
Fees swallow study is generally more expensive than barium swallow study.
Which procedure is more accurate?
Both procedures are highly accurate for diagnosing swallowing disorders.
Which procedure is more invasive?
Fees swallow study is more invasive than barium swallow study, as it requires the insertion of a fiberoptic endoscope into the throat.
Which procedure is more likely to cause side effects?
Barium swallow study is more likely to cause side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.