Unit 3.2 AP World History transports us to a vibrant era of profound transformations, where civilizations flourished and the seeds of modernity were sown. From political upheavals to cultural renaissances, this chapter in human history unfolds as a tapestry of interconnected events and ideas that shaped the destiny of nations.
Prepare to embark on an enthralling journey through time, where we will delve into the major political, social, and economic shifts that reshaped the world. We will explore the global interactions that forged new connections and ignited cultural exchanges, and analyze the intellectual advancements that illuminated the path of human progress.
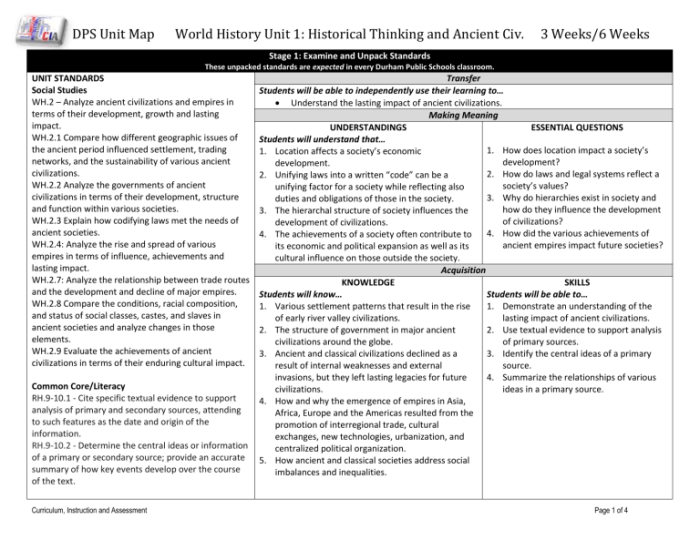
Key Historical Developments: Unit 3.2 Ap World History
Unit 3.2 encompasses a transformative era marked by profound political, social, and economic shifts. These changes shaped the course of world history and laid the groundwork for modern societies.
Politically, the rise of centralized states and empires transformed governance structures. Monarchies consolidated power, and new administrative systems emerged to manage vast territories. The development of legal codes and bureaucratic hierarchies brought order and stability to societies.
Economic Changes
Economic changes were equally significant. The expansion of trade and commerce fueled the growth of urban centers and the emergence of a global economy. New technologies, such as the compass and astrolabe, facilitated exploration and the establishment of trade routes connecting different parts of the world.
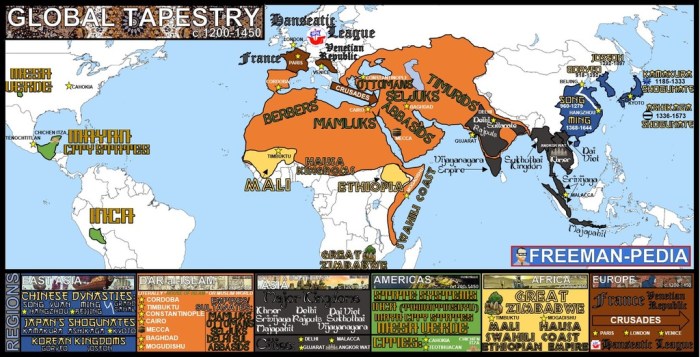
Unit 3.2 of AP World History explores the significant cultural, political, and economic developments that shaped the world from 1200 to 1450. If you’re looking for assistance with this unit, check out the eric a disparu answer key . It provides valuable insights and resources that can enhance your understanding of this fascinating historical period.
Continuing our exploration of Unit 3.2, we’ll delve into the rise of empires, the spread of religions, and the development of new technologies that transformed the medieval world.
Social Changes
Socially, the rise of monotheistic religions, such as Christianity and Islam, profoundly influenced people’s beliefs and values. These religions emphasized spiritual salvation, communal identity, and social welfare, shaping the moral fabric of societies.
Global Interactions and Connections
During Unit 3.2, the world witnessed a surge in interactions and connections between different regions, fostering cultural exchange, trade, and the spread of ideas. These interactions shaped the course of history, leaving a lasting impact on societies around the globe.
Key Players and their Roles
The key players in these interactions included:
- Merchants and traders:They facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies between different regions.
- Missionaries and explorers:They spread religious beliefs, explored new lands, and established connections between distant cultures.
- Diplomats and ambassadors:They fostered diplomatic relations and negotiated treaties, promoting cooperation and understanding.
- Empires and states:They played a significant role in shaping the global landscape, establishing trade networks, and controlling access to resources.
Cultural and Intellectual Developments
During Unit 3.2, numerous cultural and intellectual advancements reshaped societies and influenced the course of history. These advancements included the rise of new religions, the development of new philosophies, and the emergence of innovative artistic styles.
Spread of Monotheistic Religions
The spread of monotheistic religions, such as Christianity, Islam, and Buddhism, had a profound impact on societies. These religions introduced new ethical and moral codes, which influenced laws, social norms, and artistic expressions. They also contributed to the development of centralized states and the rise of empires.
Emergence of New Philosophies
The period also witnessed the emergence of new philosophies, such as Confucianism, Taoism, and Legalism in China, and Stoicism and Epicureanism in Greece. These philosophies provided frameworks for understanding the world and human nature, and influenced political, economic, and social systems.
Artistic Innovations
Significant artistic innovations occurred during this period, including the development of new architectural styles, such as Gothic architecture in Europe and Buddhist temples in Asia. Artists also experimented with new techniques and materials, leading to the creation of stunning works of art that continue to inspire and awe.
Impact on Society and History
These cultural and intellectual advancements had a lasting impact on societies and the course of history. They shaped social structures, influenced political systems, and fostered the development of new ideas and technologies. They also contributed to the creation of a more interconnected and culturally diverse world.
Causes and Consequences of Major Events
During Unit 3.2, several significant events occurred that shaped the course of world history. These events had profound causes and consequences, which continue to impact the world today.
The Columbian Exchange
The Columbian Exchange refers to the widespread exchange of plants, animals, diseases, and ideas between the Americas, Europe, and Africa following Christopher Columbus’s voyages in the late 15th century.
- Causes:
- European exploration and colonization of the Americas
- Desire for new resources and trade goods
- Consequences:
- Introduction of new crops and livestock to the Americas (e.g., corn, potatoes, horses, cattle)
- Spread of diseases such as smallpox and measles to the Americas, devastating indigenous populations
- Transfer of African slaves to the Americas, leading to the development of the transatlantic slave trade
- Cultural exchange and the spread of new ideas and technologies
The Reformation
The Reformation was a religious movement that began in Europe in the 16th century, leading to the establishment of Protestantism and the division of Western Christianity.
- Causes:
- Criticism of Catholic Church practices and corruption
- Spread of humanist ideas and the desire for religious reform
- Political and economic factors, such as the rise of nation-states and the desire for independence from papal authority
- Consequences:
- Religious wars and conflicts across Europe
- Division of Western Christianity into Protestantism and Catholicism
- Rise of religious toleration and the concept of individual conscience
- Influence on political and social structures in Europe
The Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a period of intellectual and scientific advancement that began in Europe in the 16th and 17th centuries, leading to the development of modern science.
- Causes:
- Renaissance humanism and the emphasis on reason and observation
- New technologies and instruments, such as the telescope and microscope
- Support from wealthy patrons and governments
- Consequences:
- Development of new scientific theories and laws
- Advancements in mathematics, physics, astronomy, and other fields
- Challenged traditional beliefs and authorities
- Laid the foundation for the Industrial Revolution and modern technology
Primary Source Analysis

Primary sources provide valuable insights into the past, allowing historians to understand events and perspectives from the time. In this section, we will analyze a primary source document from Unit 3.2 and explore its context, significance, and limitations.The document we will examine is a letter written by Hernán Cortés to King Charles V of Spain in 1520. In this letter, Cortés describes his conquest of the Aztec Empire and provides his perspective on the events that unfolded.
Context
Cortés’s letter was written shortly after his conquest of the Aztec capital, Tenochtitlan. The letter aimed to inform the Spanish king about the events that had transpired and to justify Cortés’s actions. Cortés portrayed himself as a loyal servant of the crown and emphasized the wealth and resources that could be gained from the conquest.
Significance
Cortés’s letter is a significant historical document for several reasons. Firstly, it provides a firsthand account of the conquest of the Aztec Empire, one of the most significant events in world history. Secondly, it sheds light on the motivations and perspectives of the Spanish conquistadors.
Thirdly, it highlights the impact of European colonization on indigenous societies.
Limitations, Unit 3.2 ap world history
While Cortés’s letter is a valuable source of information, it is important to be aware of its limitations. As a primary source, it is inherently subjective and may not provide a complete or unbiased account of events. Additionally, Cortés had a vested interest in presenting himself and his actions in a favorable light.
Comparative Analysis
Unit 3.2 of AP World History explores various perspectives on historical events and developments. By examining different viewpoints, historians gain a more comprehensive understanding of the past. This analysis helps identify biases, consider alternative interpretations, and appreciate the complexity of historical narratives.
One key topic in Unit 3.2 is the rise and spread of Islam. Different perspectives exist on the causes and consequences of this event. Some scholars emphasize the religious and spiritual motivations of early Muslims, while others highlight political and economic factors.
Political Factors
- The unification of Arabia under the leadership of Muhammad created a powerful political force.
- The conquest of neighboring territories expanded the Islamic empire and provided access to resources.
- The establishment of the caliphate provided a centralized government and administrative system.
Religious Factors
- The teachings of Islam, including the belief in one God and the importance of submission, resonated with many people.
- The message of Islam offered hope and salvation to those who felt oppressed or marginalized.
li>The spread of Islam was facilitated by missionaries and traders who carried the message to different regions.
Historical Significance
Unit 3.2 explores a pivotal period in world history, marked by profound transformations that reshaped global landscapes and set the stage for subsequent developments.
The events and developments of this period laid the foundations for modern world order, shaped cultural and intellectual currents, and ignited global interactions that continue to reverberate today.
Global Interactions and Connections
The expansion of European empires during this period led to increased global trade, cultural exchange, and the spread of new technologies. This interconnectedness fostered new economic systems, cultural influences, and political alliances that transcended regional boundaries.
- The Columbian Exchange brought new crops, animals, and diseases between the Americas and Europe, transforming global agriculture and diets.
- The rise of global trade networks facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies, leading to the development of new industries and economic interdependence.
- European colonization of the Americas, Africa, and Asia had far-reaching consequences, including the displacement of indigenous populations and the establishment of new colonial societies.
Cultural and Intellectual Developments
The Renaissance and Reformation sparked a surge in artistic, intellectual, and religious innovation. These movements challenged traditional beliefs, promoted individualism, and laid the groundwork for the Scientific Revolution and Enlightenment.
- The Renaissance emphasized humanism, classical learning, and artistic expression, leading to masterpieces in painting, sculpture, and literature.
- The Reformation challenged the authority of the Catholic Church and led to the rise of Protestantism, fostering religious pluralism and political upheaval.
- The Scientific Revolution marked a shift from traditional beliefs to empirical observation and experimentation, laying the foundations for modern science and technology.
FAQ Explained
What are the key political changes that occurred during Unit 3.2?
The rise of centralized states, the decline of feudalism, and the emergence of new political ideologies.
How did global interactions shape the course of Unit 3.2?
Trade, exploration, and cultural exchange led to the spread of ideas, technologies, and religions across vast distances.
What were some of the major cultural and intellectual advancements of Unit 3.2?
The development of writing, the rise of organized religions, and the flourishing of artistic and scientific achievements.