An oxygen atom has a mass of 2.66 – As an oxygen atom takes center stage with a mass of 2.66, this exploration delves into the significance of its atomic structure, unraveling its role in chemical reactions, biological processes, and scientific applications. Brace yourself for an enlightening journey into the world of oxygen atoms.
Delving deeper, we will uncover the intricate relationship between the mass of oxygen atoms and their atomic structure, exploring how this mass influences chemical reactions and metabolic processes. Moreover, we will delve into the fascinating world of oxygen isotopes, examining their impact on the properties of oxygen-containing compounds and their diverse applications.
Oxygen Atom’s Properties
Oxygen, an essential element for life on Earth, boasts a distinctive atomic structure that influences its properties and behavior. Understanding the mass, atomic number, and atomic weight of oxygen provides valuable insights into its chemical nature and interactions.
Atomic Mass
The oxygen atom’s mass of 2.66 atomic mass units (amu) plays a crucial role in determining its isotopic composition and chemical reactivity. The atomic mass represents the average mass of all naturally occurring isotopes of oxygen, weighted by their relative abundance.
Atomic Number and Atomic Weight
The atomic number of oxygen is 8, indicating the number of protons in its nucleus. This value remains constant for all isotopes of oxygen. The atomic weight, which is close to the atomic mass, represents the average mass of an oxygen atom relative to the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
Oxygen’s atomic weight is approximately 16 amu.
Relationship between Mass and Atomic Structure
The mass of an atom is primarily determined by the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. Protons and neutrons have nearly equal masses, while electrons have a negligible mass. Therefore, the atomic mass of oxygen reflects the combined mass of its protons and neutrons, providing valuable information about its nuclear composition.
Role in Chemical Reactions
Oxygen atoms play a crucial role in chemical reactions, particularly in combustion reactions, where they combine with other elements to release energy.
The mass of oxygen atoms significantly affects the rate of chemical reactions. The more oxygen atoms available, the faster the reaction proceeds. This is because oxygen atoms act as electron acceptors, facilitating the transfer of electrons between reactants and promoting the formation of new chemical bonds.
Examples of Chemical Reactions Involving Oxygen Atoms
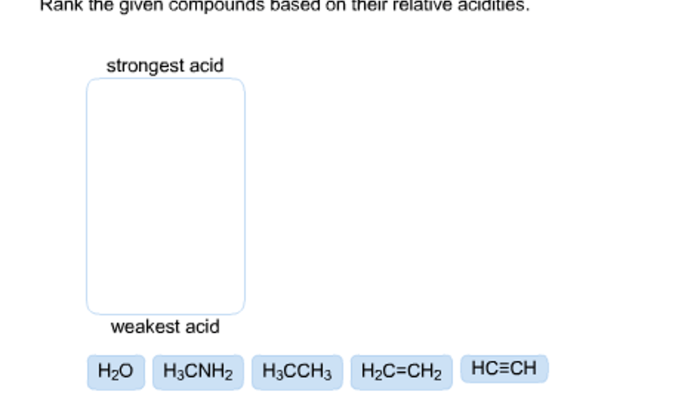
- Combustion of methane: CH 4+ 2O 2→ CO 2+ 2H 2O
- Respiration in living organisms: C 6H 12O 6+ 6O 2→ 6CO 2+ 6H 2O
- Rusting of iron: 4Fe + 3O 2→ 2Fe 2O 3
Biological Importance
Oxygen atoms play a crucial role in cellular respiration, the process by which cells convert glucose into energy. During cellular respiration, oxygen atoms are used as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, a series of proteins that transfer electrons and generate energy in the form of ATP.The
mass of oxygen atoms influences metabolic processes because it affects the efficiency of cellular respiration. Heavier oxygen atoms, such as the isotope 18O, can slow down the rate of cellular respiration, while lighter oxygen atoms, such as 16O, can speed it up.
This is because the mass of the oxygen atom affects the vibrational frequency of the oxygen-carbon bond, which in turn affects the rate of electron transfer.Biological processes that rely on oxygen atoms include:
- Cellular respiration: Oxygen atoms are essential for the final step of cellular respiration, the electron transport chain, which generates ATP.
- Metabolism: Oxygen atoms are involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
- Immune function: Oxygen atoms are required for the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are used by immune cells to kill bacteria and viruses.
- Wound healing: Oxygen atoms are necessary for the formation of new blood vessels and the healing of wounds.
Isotopes of Oxygen
Oxygen has three naturally occurring isotopes: 16O, 17O, and 18O. These isotopes differ in their neutron count, with 16O having eight neutrons, 17O having nine neutrons, and 18O having ten neutrons.
The isotopic mass of oxygen affects the properties of oxygen-containing compounds. For example, compounds containing 18O are slightly heavier than those containing 16O. This difference in mass can be used to study various processes, such as the exchange of oxygen atoms between different molecules.
Applications of Oxygen Isotopes, An oxygen atom has a mass of 2.66
Oxygen isotopes have a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Paleoclimatology:Oxygen isotope ratios in ice cores and ocean sediments are used to reconstruct past climate conditions.
- Hydrology:Oxygen isotope ratios in water samples are used to study the movement and origin of water.
- Geochemistry:Oxygen isotope ratios in rocks are used to determine the age and origin of rocks.
- Medicine:Oxygen isotopes are used in medical imaging techniques, such as PET scans, to study metabolism and diagnose diseases.
Applications in Science and Industry: An Oxygen Atom Has A Mass Of 2.66
Oxygen atoms play a crucial role in various scientific and industrial processes. Their unique properties make them essential for applications in welding, cutting, and other industries.
Uses in Welding and Cutting
In welding and cutting processes, oxygen atoms are used to create high temperatures necessary for joining or separating metals. The mass of oxygen atoms affects the efficiency of these processes.
- Higher mass:Heavier oxygen atoms release more energy when combined with fuel gases, resulting in higher temperatures and faster cutting or welding speeds.
- Lower mass:Lighter oxygen atoms provide a more precise and controlled cut or weld, but at a slower rate.
Industrial Applications
Oxygen atoms are utilized in a wide range of industrial applications, including:
- Steelmaking:Oxygen is injected into molten iron to remove impurities and produce steel.
- Glass production:Oxygen is used to melt and shape glass.
- Chemical synthesis:Oxygen is used as a reactant in the production of chemicals such as plastics, pharmaceuticals, and fertilizers.
- Medical applications:Oxygen is essential for medical treatments, including anesthesia, surgery, and oxygen therapy.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the significance of the mass of an oxygen atom?
The mass of an oxygen atom, 2.66, plays a crucial role in determining its chemical properties and reactivity, influencing the rates of reactions and the formation of various compounds.
How does the mass of oxygen atoms affect chemical reactions?
The mass of oxygen atoms influences the rate and efficiency of chemical reactions, particularly combustion reactions. The availability and reactivity of oxygen atoms impact the speed and completeness of these reactions.
What is the role of oxygen atoms in biological processes?
Oxygen atoms are indispensable for cellular respiration, the process by which cells generate energy. The mass of oxygen atoms affects the metabolic rate and efficiency of this vital biological function.