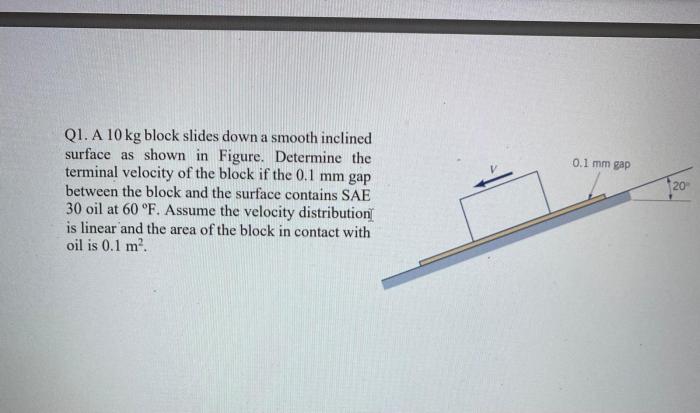
Embark on an illuminating journey with anatomy of a wave worksheet answers, an indispensable resource for comprehending the intricacies of wave behavior. This comprehensive guide unveils the fundamental components, diverse types, and captivating properties of waves, equipping you with a profound understanding of their dynamic nature.
Delve into the anatomy of a wave, dissecting its crest, trough, wavelength, amplitude, and period. Explore the contrasting characteristics of transverse and longitudinal waves, deciphering their unique properties and real-world applications. Discover the intricate relationship between wave frequency, velocity, and energy, unraveling the factors that govern their behavior.
Anatomy of a Wave: Components and Terminology
Waves are disturbances that propagate through a medium, transferring energy without transporting matter. The fundamental components of a wave are:
- Crest:The highest point of a wave.
- Trough:The lowest point of a wave.
- Wavelength:The horizontal distance between two consecutive crests or troughs.
- Amplitude:The vertical distance between the crest and the trough, representing the maximum displacement from the equilibrium position.
- Period:The time it takes for a wave to complete one cycle (from crest to crest or trough to trough).
These components are crucial in describing wave behavior and understanding wave phenomena.
Types of Waves: Transverse and Longitudinal, Anatomy of a wave worksheet answers
Waves can be classified into two main types based on their direction of oscillation relative to the direction of wave propagation:
- Transverse Waves:The particles of the medium oscillate perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. Examples include light waves, electromagnetic waves, and water waves on the surface of a liquid.
- Longitudinal Waves:The particles of the medium oscillate parallel to the direction of wave propagation. Examples include sound waves and seismic waves.
Transverse waves exhibit polarization, while longitudinal waves do not.
Wave Properties: Frequency, Velocity, and Energy
Important properties of waves include:
- Frequency:The number of waves passing a given point per unit time, measured in hertz (Hz). It is inversely proportional to the wavelength.
- Velocity:The speed at which a wave travels through a medium, dependent on the medium’s properties. Velocity is directly proportional to wavelength and frequency.
- Energy:The energy carried by a wave is proportional to the square of its amplitude and frequency.
Understanding these properties is essential for analyzing wave behavior and applications.
Wave Interactions: Reflection, Refraction, and Diffraction
When waves encounter boundaries or obstacles, they undergo various interactions:
- Reflection:Waves bouncing off a surface, such as light reflecting off a mirror or sound waves reflecting off a wall.
- Refraction:Waves bending as they pass from one medium to another, such as light bending as it enters water from air.
- Diffraction:Waves spreading out as they pass through an opening or around an obstacle, such as water waves diffracting around a pier.
These interactions are crucial in understanding wave behavior in various contexts.
Wave Applications in Science and Technology
Waves have numerous applications in various scientific fields and technologies:
- Acoustics:Studying sound waves, including noise control, musical instruments, and medical imaging.
- Optics:Investigating light waves, including lens design, optical communications, and laser technology.
- Oceanography:Analyzing water waves, including wave energy, coastal erosion, and ocean currents.
- Ultrasound:Using high-frequency sound waves for medical imaging and non-destructive testing.
- Radar:Utilizing electromagnetic waves to detect objects and measure distances.
- Telecommunications:Employing electromagnetic waves for wireless communication, including cell phones and Wi-Fi.
The understanding and application of waves are essential in advancing various fields and technologies.
Commonly Asked Questions: Anatomy Of A Wave Worksheet Answers
What is the significance of wave amplitude?
Wave amplitude determines the intensity or strength of a wave, directly influencing its energy and observable effects.
How does wave frequency impact wave behavior?
Wave frequency dictates the number of wave cycles that occur within a specific time frame, influencing the wave’s pitch or perceived sound.