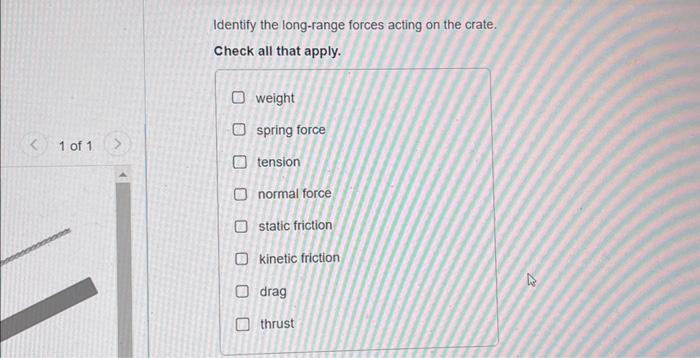
As we embark on the exploration of ‘identify the long-range forces acting on the crate,’ we uncover a captivating interplay of forces that shape the crate’s behavior. From the pervasive influence of gravity to the subtle resistance of air, this analysis unveils the intricate forces that orchestrate the crate’s motion.
Delving into the realm of external forces, we dissect the gravitational pull that anchors the crate to the earth’s embrace. We unravel the intricate dance between friction and motion, examining how this frictional force impedes the crate’s journey. Furthermore, we illuminate the role of air resistance, a subtle yet persistent force that molds the crate’s trajectory.
Long-Range Forces Acting on the Crate: Identify The Long-range Forces Acting On The Crate
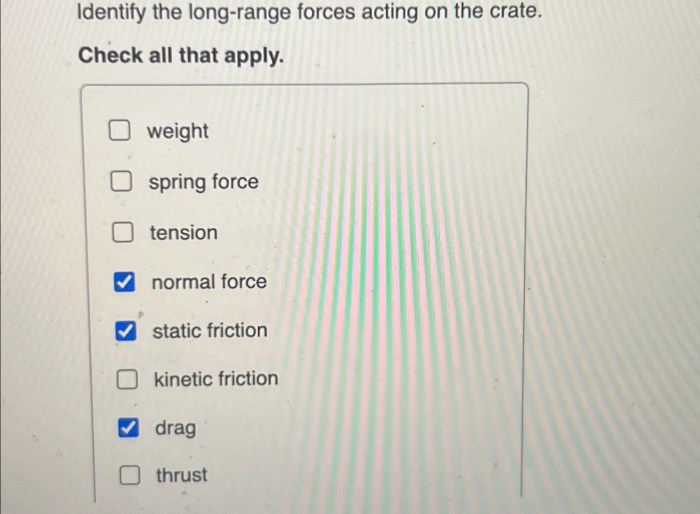
Long-range forces are those that act over large distances, often without any physical contact between the objects involved. The most common long-range forces are gravitational force, electric force, and magnetic force. In the case of a crate resting on a surface, the primary long-range force acting on it is gravitational force.
Gravitational Force
Gravitational force is a fundamental force that exists between any two objects with mass. It is a conservative force, meaning that it does not depend on the path taken by the objects as they move. The magnitude of the gravitational force between two objects is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.In
the case of a crate resting on a surface, the gravitational force acts between the crate and the Earth. The direction of the gravitational force is downward, towards the center of the Earth. The magnitude of the gravitational force is given by the equation:“`F_g = G
- m_1
- m_2 / r^2
“`where:* F_g is the gravitational force
- G is the gravitational constant (6.674 × 10^-11 N m^2 kg^-2)
- m_1 is the mass of the crate
- m_2 is the mass of the Earth
- r is the distance between the center of the crate and the center of the Earth
Friction, Identify the long-range forces acting on the crate
Friction is a force that opposes the relative motion of two surfaces in contact. It is a non-conservative force, meaning that it depends on the path taken by the objects as they move. The magnitude of the frictional force is directly proportional to the normal force (the force perpendicular to the surfaces in contact) and the coefficient of friction.In
the case of a crate resting on a surface, the frictional force acts between the crate and the surface. The direction of the frictional force is opposite to the direction of motion (or potential motion) of the crate. The magnitude of the frictional force is given by the equation:“`F_f = μ
N
“`where:* F_f is the frictional force
- μ is the coefficient of friction
- N is the normal force
Air Resistance
Air resistance is a force that opposes the motion of an object through a fluid (such as air). It is a non-conservative force, meaning that it depends on the path taken by the object as it moves. The magnitude of the air resistance force is directly proportional to the velocity of the object and the cross-sectional area of the object.In
the case of a crate moving through air, the air resistance force acts in the opposite direction to the motion of the crate. The magnitude of the air resistance force is given by the equation:“`F_a = 1/2
- ρ
- v^2
- A
“`where:* F_a is the air resistance force
- ρ is the density of the fluid
- v is the velocity of the object
- A is the cross-sectional area of the object
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary long-range force acting on the crate?
Gravity
How does friction affect the crate’s motion?
Friction opposes the crate’s motion, reducing its velocity and causing it to eventually stop.
What is the role of air resistance in crate dynamics?
Air resistance acts as a drag force that opposes the crate’s motion, reducing its acceleration and velocity.