Similarities between democratic vs. authoritarian govts – Similarities between democratic and authoritarian governments, though seemingly contradictory, offer a nuanced understanding of the complex spectrum of political systems. This essay delves into the structural, participatory, economic, foreign policy, and stability aspects shared by these seemingly disparate regimes, uncovering the subtle yet significant parallels that shape their governance models.
Exploring the distribution of power, citizen participation, economic principles, foreign policy approaches, and mechanisms for stability and change, this analysis unveils the intricate interplay between democratic and authoritarian elements, challenging conventional dichotomies and providing a deeper appreciation of the complexities of political systems.
Structural Similarities
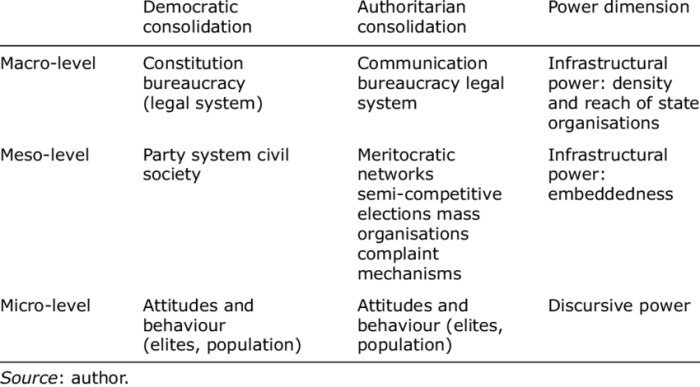
In both democratic and authoritarian governments, power is distributed among various branches and institutions. In democracies, power is typically divided among the executive, legislative, and judicial branches, with checks and balances in place to prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful.
In authoritarian governments, power is concentrated in the hands of a single ruler or a small group of elites, with limited or no checks and balances.
Elected and Appointed Officials, Similarities between democratic vs. authoritarian govts
In democracies, elected officials are chosen by the people through regular elections. These officials are responsible for representing the interests of their constituents and making decisions on their behalf. Appointed officials, on the other hand, are chosen by the executive branch and are responsible for carrying out the policies of the government.
Citizen Participation and Rights
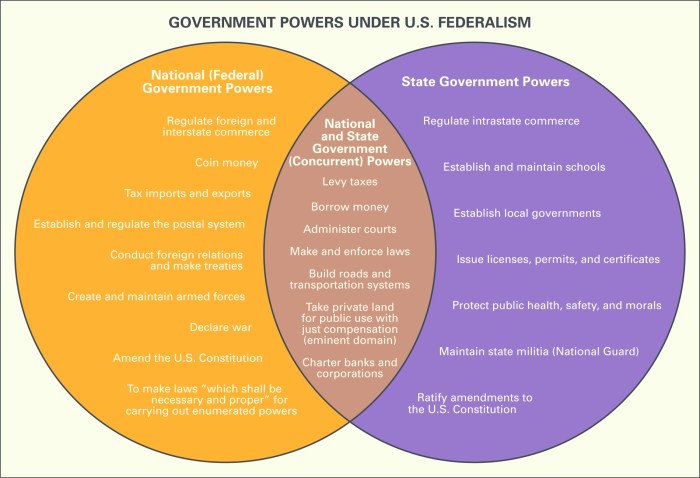
In democracies, citizens have a high level of participation in government through voting, elections, and other forms of political engagement. They also enjoy a wide range of individual rights and freedoms, such as freedom of speech, assembly, and religion. In authoritarian governments, citizen participation is often restricted, and individual rights and freedoms are often suppressed.
Methods of Citizen Involvement
- Voting and elections
- Protests and demonstrations
- Lobbying and advocacy
Protection of Individual Rights
In democracies, individual rights are protected by the constitution and enforced by the courts. In authoritarian governments, individual rights are often not protected, and the government may arbitrarily detain, torture, or even kill its citizens.
Economic Systems
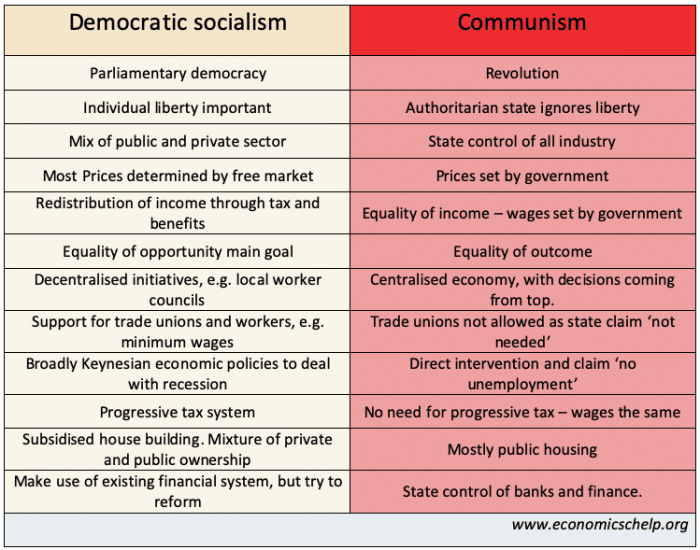
Democratic governments typically embrace free market principles, with limited government intervention in the economy. Authoritarian governments, on the other hand, often have a more interventionist approach, with the government playing a significant role in directing the economy.
Economic Principles
- Democratic governments:Free market principles, limited government intervention
- Authoritarian governments:Interventionist approach, government plays a significant role
Policy Formulation and Implementation
In democracies, economic policies are typically formulated by elected officials and implemented by appointed officials. In authoritarian governments, economic policies are often formulated and implemented by the ruling elite.
Foreign Policy and International Relations: Similarities Between Democratic Vs. Authoritarian Govts
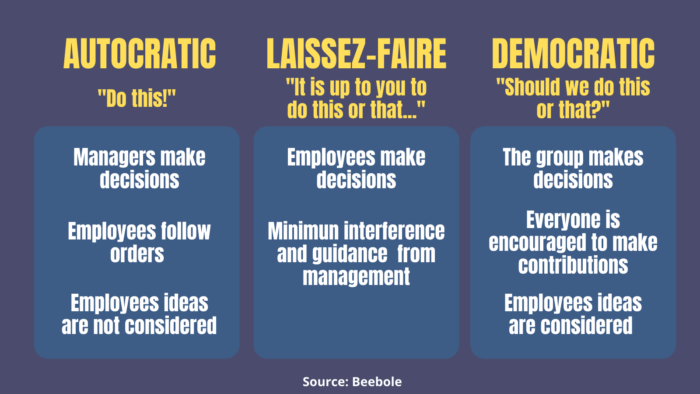
Democratic governments tend to have a more multilateral approach to foreign policy, seeking to cooperate with other countries and international organizations. Authoritarian governments, on the other hand, often have a more unilateral approach, acting independently of other countries.
Approaches to Foreign Policy
- Democratic governments:Multilateral approach, cooperation with other countries
- Authoritarian governments:Unilateral approach, acting independently
Decision-Making Processes
In democracies, foreign policy decisions are typically made through a consultative process involving elected officials, appointed officials, and experts. In authoritarian governments, foreign policy decisions are often made by the ruling elite with little or no input from others.
Stability and Change
Democratic governments tend to be more stable than authoritarian governments, as they have built-in mechanisms for peaceful transfer of power and resolution of conflicts. Authoritarian governments, on the other hand, are often more unstable, as they rely on force and coercion to maintain control.
Factors Contributing to Stability
- Peaceful transfer of power
- Resolution of conflicts through dialogue and compromise
- Rule of law and respect for human rights
Mechanisms for Political Succession
In democracies, political succession typically occurs through regular elections. In authoritarian governments, political succession is often less clear and may involve violent power struggles.
Clarifying Questions
What is the primary difference between democratic and authoritarian governments?
The primary difference lies in the distribution of power and the level of citizen participation. Democratic governments empower citizens through elections and representative bodies, while authoritarian governments concentrate power in the hands of a single ruler or a small elite.
Can authoritarian governments be stable?
Yes, authoritarian governments can achieve stability through various means, such as suppression of dissent, control of the media, and economic development. However, this stability is often fragile and can be challenged by internal and external pressures.
Do democratic governments always protect individual rights?
While democratic governments generally uphold individual rights, these rights can be restricted in times of crisis or under certain circumstances. The level of protection varies depending on the specific democratic system and the balance of power between different branches of government.