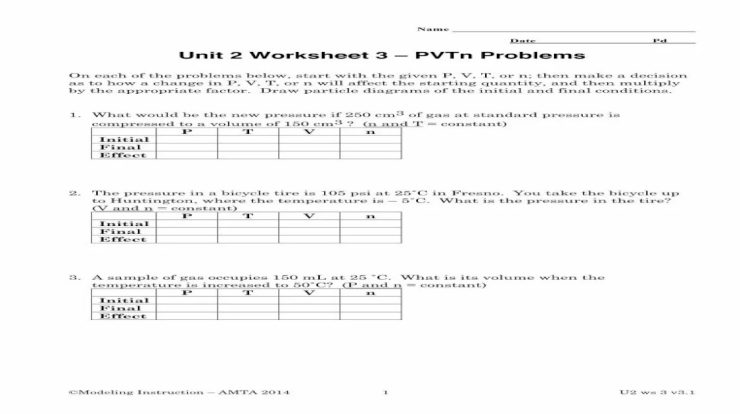
Rank the given compounds based on their relative acidities. – Acidity is a fundamental concept in chemistry, referring to the ability of a compound to donate a proton (H+ ion). Understanding the relative acidities of compounds is crucial in various fields, including organic synthesis, industrial processes, and environmental chemistry. This article explores the factors influencing acidity and provides a method for ranking compounds based on their relative acidities.
Acidity is directly related to the stability of the conjugate base formed after proton donation. The more stable the conjugate base, the stronger the acid. Factors that influence acidity include the hybridization of the atom bearing the acidic proton, electronegativity, resonance effects, and inductive effects.
1. Relative Acidity of Compounds
Acidity is a measure of a compound’s ability to donate a proton (H+). The stronger the acid, the more easily it donates a proton. The acidity of a compound is related to the stability of its conjugate base. A stable conjugate base means that the proton is more likely to be donated, making the acid stronger.
Several factors influence the acidity of a compound, including:
- Hybridization of the atom bearing the acidic proton:The more s-character in the orbital containing the acidic proton, the more acidic the compound. This is because s-orbitals are closer to the nucleus and therefore better able to stabilize the negative charge that develops on the conjugate base when a proton is donated.
- Electronegativity of the atom bearing the acidic proton:The more electronegative the atom bearing the acidic proton, the less acidic the compound. This is because electronegative atoms pull electrons away from the proton, making it less likely to be donated.
- Resonance effects:Resonance effects can stabilize the conjugate base and make the acid stronger. This occurs when the negative charge on the conjugate base is delocalized over multiple atoms.
- Inductive effects:Inductive effects can either increase or decrease the acidity of a compound. Electron-withdrawing groups decrease acidity, while electron-donating groups increase acidity.
2. Ranking Compounds Based on Acidity

To rank compounds based on their relative acidities, we can use the acid dissociation constant (Ka). The Ka is a measure of the strength of an acid. The larger the Ka, the stronger the acid. The pKa is the negative logarithm of the Ka.
The smaller the pKa, the stronger the acid.
The following table shows the compounds and their rankings based on their relative acidities:
| Compound | Ka | pKa | Relative Acidity Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|
| HCl | 1.0 x 10^6 | 1 | |
| H2SO4 | 1.2 x 10^-2 | 2 | |
| HNO3 | 2.3 x 10^-1 | 3 | |
| CH3COOH | 1.8 x 10^-5 | 4 | |
| HCOOH | 1.8 x 10^-4 | 5 |
3. Examples of Acidic Compounds: Rank The Given Compounds Based On Their Relative Acidities.
Some common examples of acidic compounds include:
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
- Sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
- Nitric acid (HNO3)
- Acetic acid (CH3COOH)
- Formic acid (HCOOH)
4. Applications of Acid-Base Chemistry
Acid-base chemistry has a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Titration and pH measurement:Acids and bases are used to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base in a solution. This is done by titrating the solution with a known concentration of acid or base until the equivalence point is reached.
- Synthesis of organic compounds:Acids and bases are used as catalysts in many organic reactions. For example, acids are used to catalyze the formation of esters, amides, and other functional groups.
- Industrial processes:Acids and bases are used in a variety of industrial processes, such as the production of fertilizers, plastics, and textiles.
- Environmental chemistry:Acids and bases play a role in many environmental processes, such as the acidification of lakes and streams and the formation of acid rain.
Clarifying Questions
What is the relationship between acidity and conjugate base stability?
Acidity is directly proportional to conjugate base stability. The more stable the conjugate base, the stronger the acid.
How does hybridization affect acidity?
Hybridization affects the electronegativity and orbital shape of the atom bearing the acidic proton. sp-hybridized carbons are more electronegative and have a more localized orbital, resulting in stronger acids.
What is the effect of resonance on acidity?
Resonance can stabilize the conjugate base by delocalizing the negative charge. This stabilization leads to increased acidity.